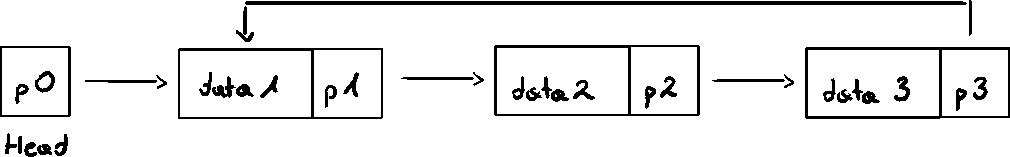
Linked Lists
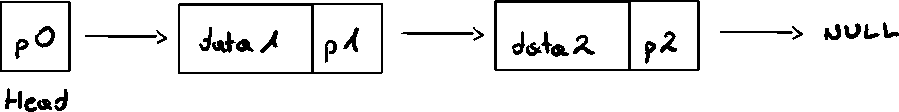
Structure
Head (first)
Address of the first node in the list
Arrow points to node address
stored in node
Down arrow in last node indicates NULL link field
First lab (23.10) will not include iterators
Second lab will include iterators
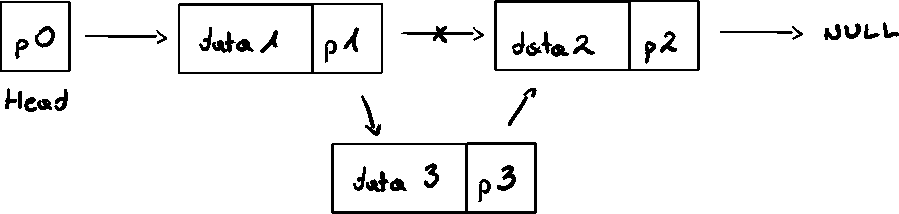
Item insertion
To insert element, we change previous node's pointer to the new node, and the new element's pointer to the next node.
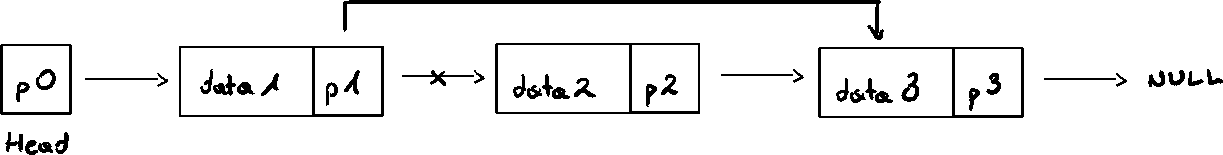
Item deletion
Memory is still occupied by node after deletion
memory is inaccessible
deallocate memory using a pointer to the node
Time complexity of operations
{cpp}class linkedListType
| function | time-complexity |
|---|---|
| isEmptyList | O(1) |
| default constructor | O(1) |
| destroyList | O(n) |
| front | O(1) |
| end | O(1) |
| initializeList | O(n) |
| O(n) | |
| length | O(1) |
| front | O(1) |
| back | O(1) |
| copyList | O(n) |
| destructor | O(n) |
| copy constructor | O(n) |
| overloading assignment operator | O(n) |
Double linked lists
Linked list in which every node has a {cpp}next pointer and a {cpp}back pointer
Every node except the last node contains address of the next node
Every node except the first node contains address of the previous node

Circular linked list
Last node points to the first node
Basic operations
- initialize list (to an empty state)
- determine if list is empty
- destroy list
- print list
- find the list length
- search for a given item
- insert item
- delete item
- copy the list
It does not matter where is the first element - advantage of the circular linked list
if (!first) return;
node *ptr = first;
do {
cout << ptr -> Key << '\n';
ptr = ptr -> next;
} while (ptr != first);
// another possibility, but requires processing of the first element once again
ptr = first;
while (ptr -> next != first) { ... }
Removing an element
The tricky part is remembering what to do when the circular linked list has only one node.
When it has multiple nodes, is it easy
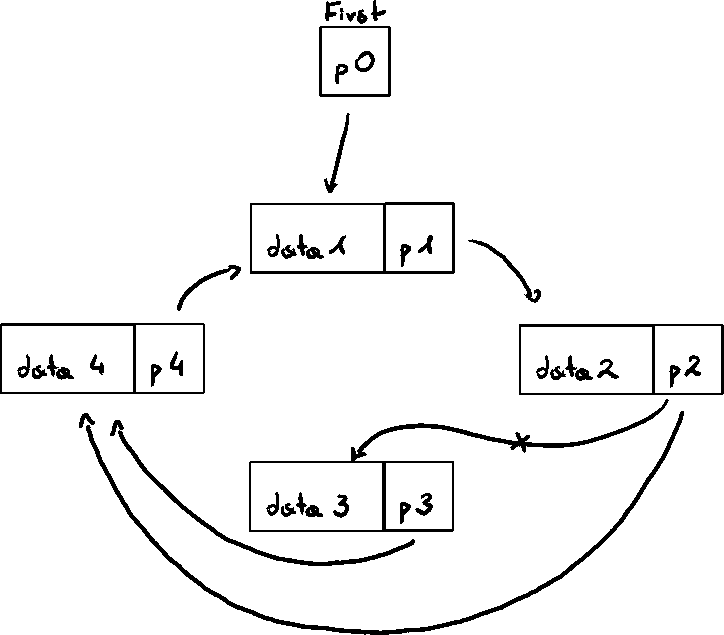
But when it has only one node
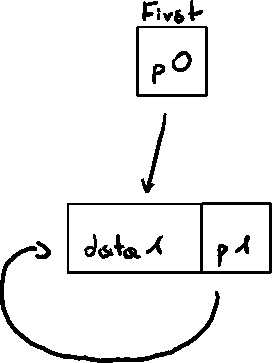
Removing the element by pointing the {cpp}next pointer to the successor of the removed node will not work, because data1 is its own successor and predecessor.
in this case, we need to make sure that {cpp}first will point to null
Another tricky thing to remember is to check whether the node we're removing is pointer do by {cpp}first. If it is, our data set gets unstable.
Linked lists with head nodes
Dual algorithms can be reduced to one
create a 'dummy' head node
server as predecessor to the data
even an empty list has a node

This head node is called sentinel
Special consideration is needed when deleting the first data-node
Traversal algorithm must be adjusted for circular linked list
Sparse polynomials
To save polynomial, we can use a normal array/linked list
but it can be very inefficient if we save each possible power like for
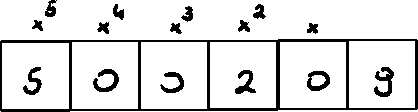
Which for big polynomials with lots of 0's will be horrible
What we can do is create a linked list with node containing x's power, value at this power and ptr to next node.
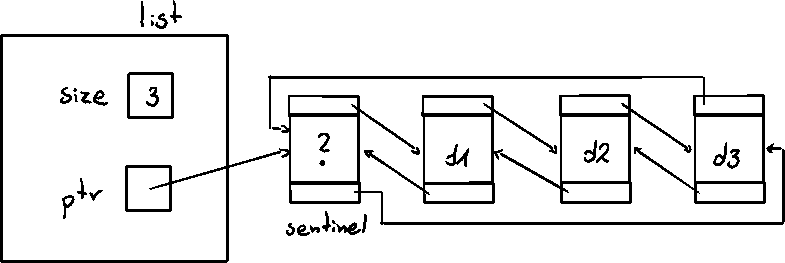
STL {cpp}list<T> class template
A sequential container
optimized for insertion and erasure at arbitrary points in the sequence
implemented as a circular doubly-linked list with head node
Comparision of {cpp}STL containers
| Property | {cpp}array |
{cpp}vector<T> |
{cpp}deque<T> |
{cpp}list<T> |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct/random access | + (perfect) | + | + (good) | X |
| Sequential access | + | + | + (good) | + |
| Insert/delete front | - (poor) | - | + | + |
| Insert/delete end | + | + | + | + |
| Insert/delete in middle | - | - | - | + |
| Overhead | lowest | low | low/med | high |
{cpp}list<T> does not support direct access (subscript operator [..]) |
BigInt design
If {cpp}INT_MAX is not enough, we can create our own data structure
First step - select a storage structure
we choose a linked list
each node contains 3 digits (for example)
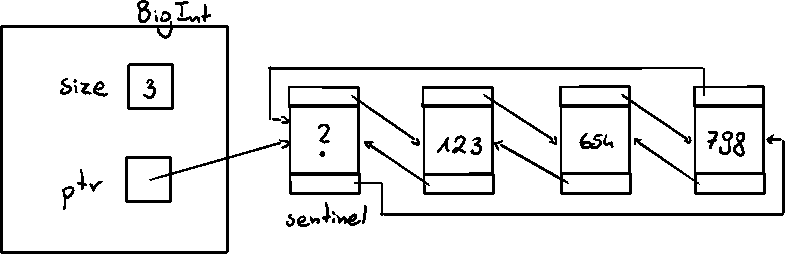
We need to override mathematical operators
keep track of carry values
Multiply ordered lists
List with multiple pointers, each pointer having other sorting
Example - user with score, player_id and birth_date
score pointers sort the list by score
player_id sort the list by ids
birth_date sort the list by dates
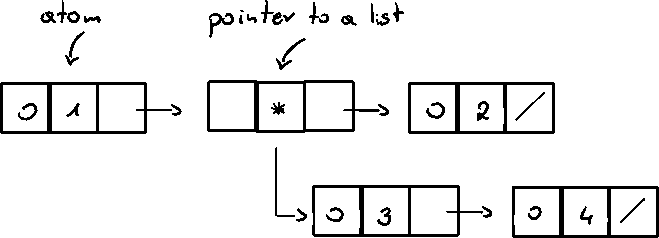
Generalized lists
List node consists of three things:
- type of value
- value / ptr to sublist
- ptr to next node
Type of value represents whether the second content is a value or a pointer to a sublist