Instantaneous power
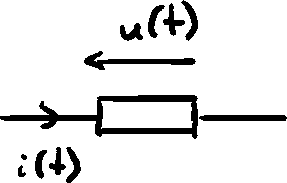
Mean power
In AC, mean power is also called real power
If , then
Examples
Inductor -
Capacitor -
Resistor -
Root Mean Square
For harmonic signal
Real power and RMS
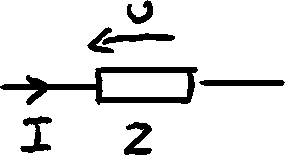
for resistor Z=R, we obtain "the same" formulas as for DC
Maximum Power Transfer theorem
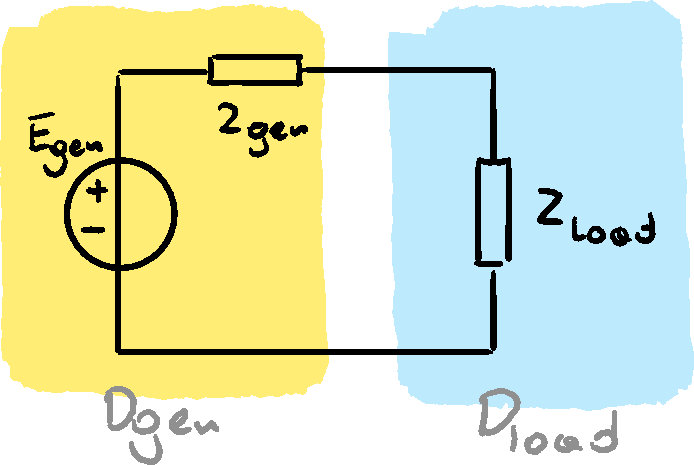
If and are const, and , then the maximal real power that can be transferred to is equal to
Such power is delivered to iff


